Ansible
Project Overview
In modern network environments, the frequent addition and removal of devices can make network management complex and prone to human error. Automation tools help streamline these processes, improve efficiency, and reduce mistakes. This project leverages Ansible, a powerful automation platform, to simplify network device configuration and management in a virtual lab environment.Objective
- Deploy EVE-NG as a virtual network lab to simulate a production environment for testing and learning.
- Establish a fully functional automation server using Ansible, specifically focused on managing and configuring network devices.
- Develop a hands-on understanding of network automation workflows, including playbook creation, execution, and verification of results.
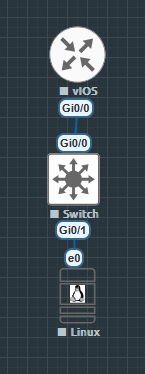
Network Topology
The network topology for this project is intentionally simple to provide a clear learning path. It consists of:
- A single Debian server hosting the Ansible automation platform.
- A single router acting as a target device for configuration tasks.
Image/s
Implementation Steps
- Set up a Virtual Machine: Installed Debian to host the Ansible automation server.
- Deploy Virtual Network Devices: Configured virtual routers and switches within the EVE-NG lab environment to act as targets for automation.
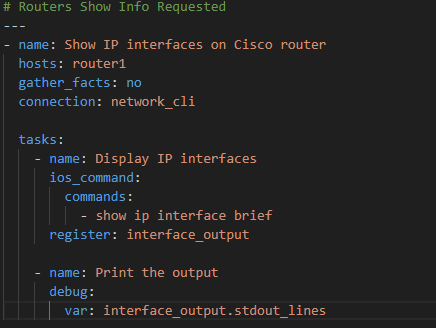
- Create Ansible Playbooks: Developed playbooks to automate repetitive tasks such as interface configuration, VLAN assignment, and basic network verification.
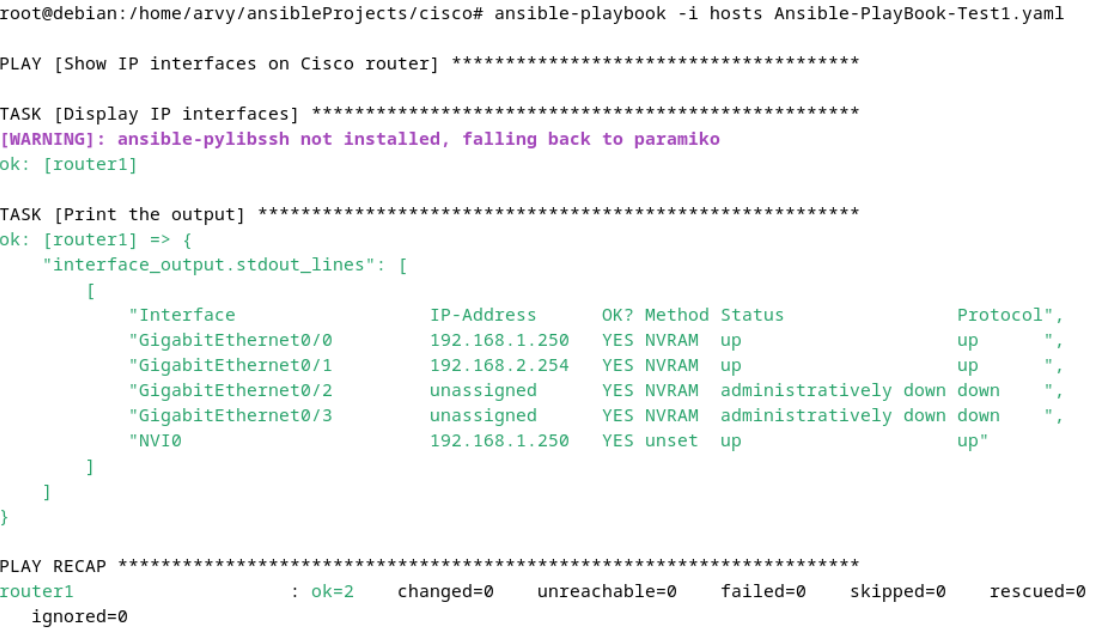
- Execute Playbooks and Display Results: Ran the playbooks and documented the outcomes to verify successful automation and identify areas for improvement.
Results
The project demonstrated successful automation of network device configuration using Ansible. The playbooks executed tasks consistently and produced predictable results, significantly reducing the time required for manual configuration.
Image/s
Automation Professional Experience
- No professional experience using Ansible.
- Automox: Worked on patch management automation, including scheduling and deployment of updates across multiple systems.
- PowerShell Scripting: Automated patch management processes by creating scripts that check for installed applications and execute updates in parallel on multiple machines, typically 10 at a time.